I did my PhD at LadHyX during 2000-2004 supervised by Jean-Marc Chomaz. My dissertation was an experimental and theoretical study of the dynamics of pancake vortices and their interaction with internal gravity waves in a strongly stratified fluid.
I did my PhD at LadHyX during 2000-2004 supervised by Jean-Marc Chomaz. My dissertation was an experimental and theoretical study of the dynamics of pancake vortices and their interaction with internal gravity waves in a strongly stratified fluid.
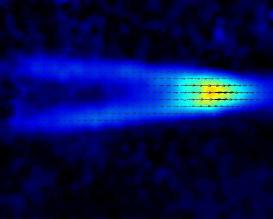
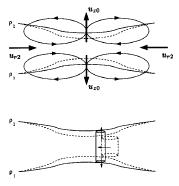
Abstract. Stably stratified fluids give rise to distinct internal wave modes and potential vorticity modes (PV). The timescales relevant to these two types of motion separate when the stratification is strong: Internal waves propagate on a fast timescale based on the buoyancy frequency (TN = N-1) while a slower timescale in terms of the horizontal advection —TA = Lh/U, where Lh and U are the horizontal length scale and mean velocity of the horizontal motions— characterizes the evolution of vortices. An illustration of the difference between these two modes can be observed in turbulent regions decaying in presence of background stable stratification : As vertical motions are suppressed, energy is either radiated as internal waves, which propagate away from the initially turbulent region, or transferred to horizontal advective motions which are finally organized as patches of potential vorticity. This thesis presents a theoretical and experimental study of the interaction between pancake vortices (representing the PV mode) and internal gravity waves in a strongly stratified fluid, and of the diffusive mechanisms of pancake vortices.
Document indexed at https://pastel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-00007046/
Continue reading “The dynamics of pancake vortices in strongly stratified fluids”
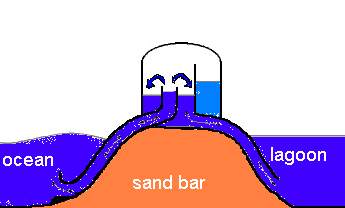
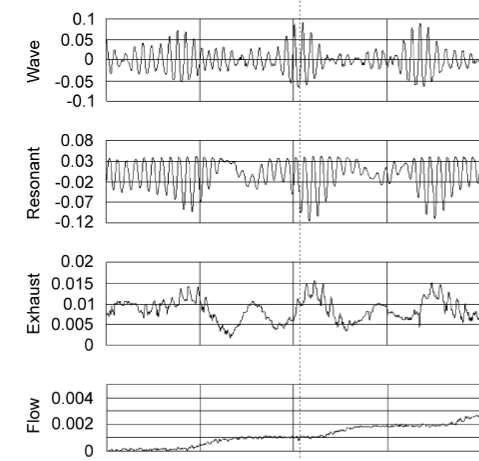 On the tuning of a wave-energy driven oscillating-water-column seawater pump to polychromatic waves
On the tuning of a wave-energy driven oscillating-water-column seawater pump to polychromatic waves