J. C. Muñoz-Hervás, B. Semin, M. Lorite-Díez, G. J. Michon, Juan D’Adamo, J.I. Jiménez-González, R. Godoy-Diana
Physical Review Fluids 10, 063903 (2025)
doi: 10.1103/8jd7-j82q
preprint: arXiv:2411.08556
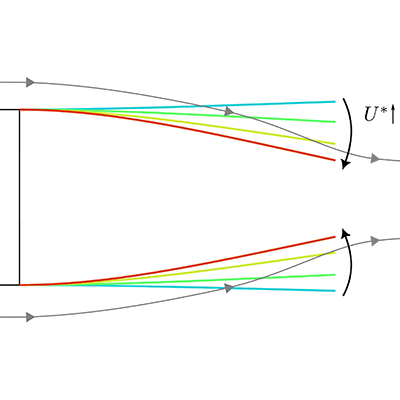
The wake flow behind blunt, D-shaped objects is an archetype to study recirculation bubbles and velocity deficits that increase drag. This has prompted interest in passive flow control methods using flexible appendages. We investigated how adding series of rigid and flexible plate-like filaments behind a D-shaped body in a water channel could modify wake dynamics and reduce drag. Using Particle Image Velocimetry to measure wake flow patterns and high-speed imaging to track filament motion, we tested various filament stiffnesses and positions across different flow velocities. The flexible filaments demonstrated passive reconfiguration in response to the flow, with tip deflection angles reaching up to 9° and vibration amplitudes of around 4° at higher flow velocities, which corresponded to reduced recirculation bubbles and decreased velocity deficits in the wake compared to cases with no filaments or rigid filaments. Interestingly, pre-curved rigid filaments matched the performance of flexible ones, suggesting that the bending motion rather than the vibration of flexible filaments drives the flow improvement, and highlighting the potential for designing effective passive flow control devices using flexible appendages in the wakes of blunt bodies.